Power Plant Equipment
"Precise Engineering, Optimum Efficiency"
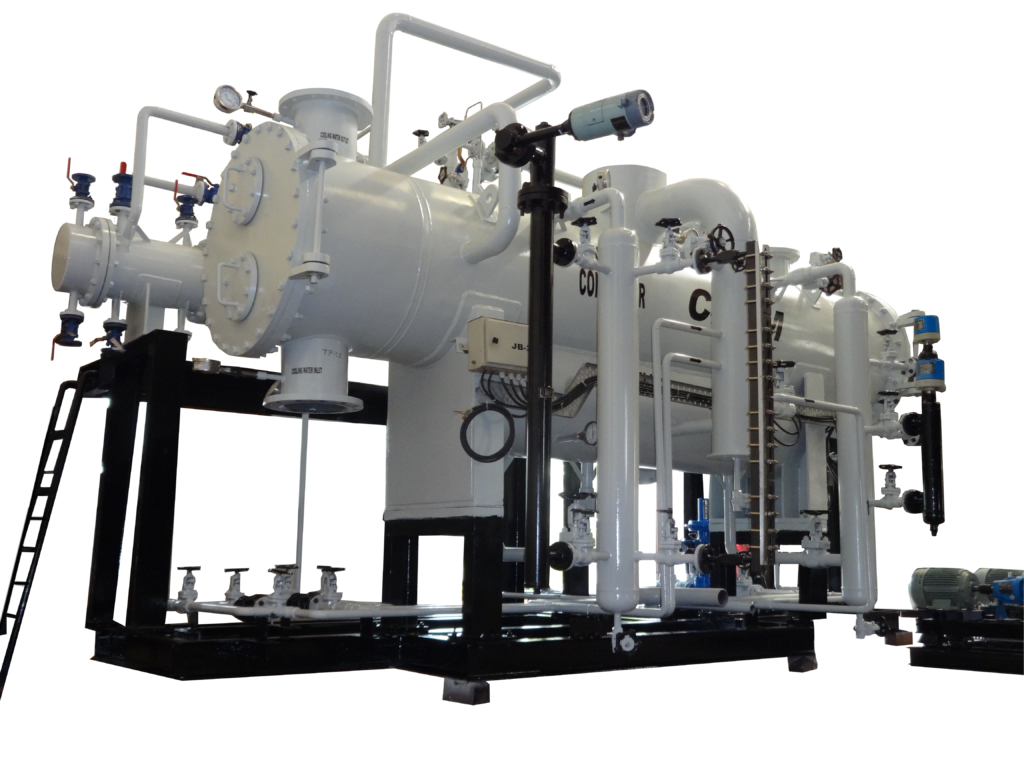
Surface Condenser
Having an experience of more than 2 decades in heat transfer equipment, Chem Process System has successfully designed & manufactured 500+ Surface Condensers. Forged with passion and commitment to providing the best to our clients, we have developed expertise in the technology for versatile yet rigid surface condensers, being able to perform under various conditions. We have designed and fabricated condensers for up to 220 TPH Capacity and fabricated rectangular condensers for up to 650 TPH. For an even larger model, it is possible to manufacture a condenser in modules assembled at the site under our guidance and supervision to complete it. Condenser size is limited by transportation feasibility. Having supplied condensers all across the Indian subcontinent, We gained experience with all kinds of geographic and atmospheric challenges to product designing and operation. We consider the site's atmospheric conditions while designing. To keep pace with the ever-changing technology, we are always on our toes to incorporate new ideas and put innovative equipment and tools into existing plant structures in order to improvise our technology and productivity to be able to deliver a product designed and fabricated with the highest standards for its ultimate area of installation and usage. We have supplied surface condensers to almost all kinds of industries and all parts of the globe including special certifications such as ASME U-Stamp, CE- PED, DOSH, CSA, TRCU (GOST) Etc.
Compatible with
- Direct condensing
- Extraction cum
- condensing Bypass dumping
Construction Features
- Integrated tube sheet
- Extended tube sheet
- Explosion bonded T/S
- Cladded Tubesheet
- Divided/Undivided Waterbox
- Skid mounted
- condensing system package
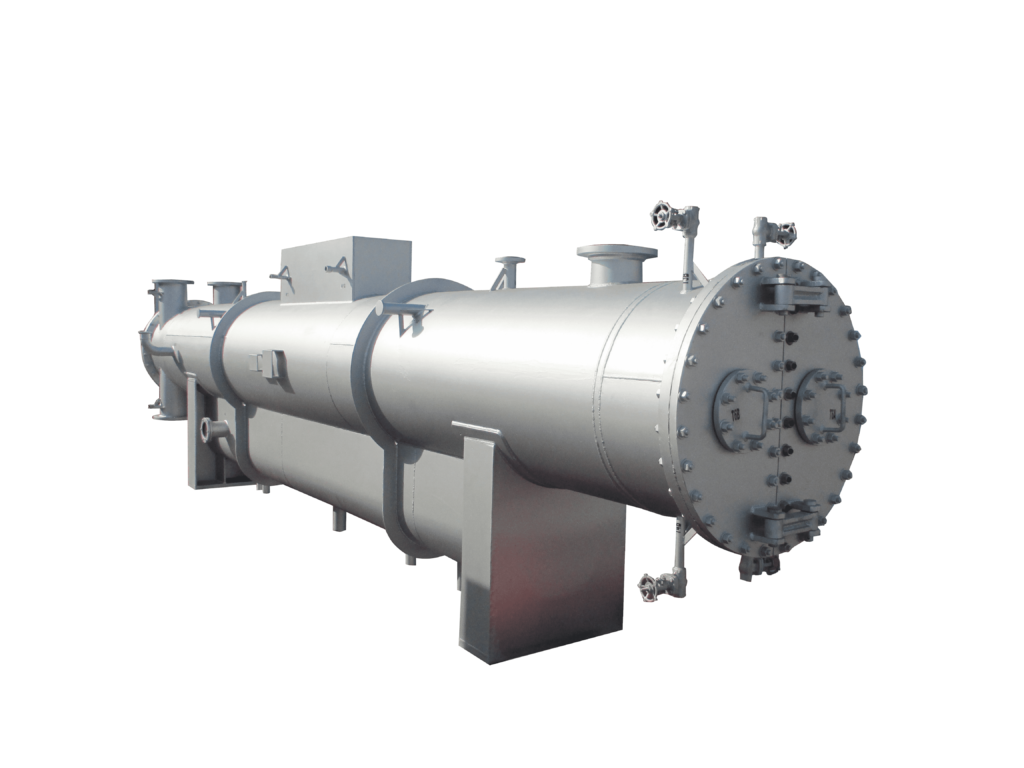
Types of condenser
- Top steam Inlet
- Axial steam Inlet
- Dual steam inlet



Feed Water Heaters
Chem Process Systems offers high quality Feed water Heaters to meet the client’s requirements in the power generation, chemical, petrochemical and marine engineering industries. We design and manufacture both low pressure and high pressure Feed water Heaters which may be installed either vertically or horizontally, depending on the plant design requirements. Conservatively designed tube bundles and proven venting concepts provide permanent protection against damage and guarantee optimal heat transfer. We offer the complete range of Feed water Heaters for nuclear and large scale conventional power plants, such as:
- U-type Feedwater Heaters
- Duplex Heaters with U-tube bundles
- Heaters with Drain Cooling and Steam Desuperheating sections
Features & Highlights
- Special constructions such as U-tube Duplex Heaters
- Optimized tube bundle venting system to enhance performance
- Design, manufacture and erection from one source
- Proven by reference
- Plant sizes from 2-150 MWe plant capacity
- Vertical or horizontal designs for both LP and HP units
- LP/HP Heaters with U-tubes
- Duplex Heaters with U-tubes
Industrial Application
- Power Generation
- Chemical
- Petrochemical
- Marine Engineering

Design
The design parameters of the Feed water Heaters are determined by the economics of design and plant requirements. Each Feed water Heater will contain one to three separate heat transfer areas or zones including the condensing, desuperheating and subcooling zones. The tube material, tube diameter and water velocity are selected based on the calculation of operational economy and safety.
- For LP heaters the tubes are expanded by rolling into the tube sheet. For HP heaters the tubes are welded to the tubesheet followed by a light expansion.
- The bundle carrier is designed such that the tubes are protected against deformation and vibration and can freely expand.
- The support plates with the tube bundles can freely move in longitudinal and cross direction, despite the unequal thermal expansion due to the hot and cold tube leg. The support plates show furthermore supports in the shape of wings, in order for lateral guidance of the bundle carrier at the inner wall of the steam shell.
- The bundle carrier consists of support plates, side metal sheets, spacers and tie- rods which can be economically assembled quickly and with little welding work.
Design Features
- Independent Desuperheating Zone Closures
- Baffle Configuration and Spacing based on Conservative Mass Velocity Criteria
- Fully enclosed Self-Venting Drains and Sub-Cooling Zones
- Liberal Sub-Cooling Zone entrance areas to permit low approach velocities which prevent flashing of Saturated Drains
- Internal, centrally located venting arrangement to provide a positive means of continuously venting condensing zone
- Channel Cover Configurations for all nozzle layouts
- Fully automated Tube-To-Tubes sheet welding procedures
- Hydraulic or Conventional Tube Expansion assuring consistently reliable Tube Joints
Types Of Feed Water Heaters
- LP (LOW PRESSURE) WATER HEATER
- HP (HIGH PRESSURE) WATER HEATER
Low-Pressure Feed water Heater
A Low-Pressure Feed water Preheater or Heater in power plants, heated with bleed steam and having a two-pass tube bundle of the tube sheet type of construction, has a carrier design for the tube bundle having side plates running parallel to the tube bundle and one or more supporting plates disposed perpendicularly to the tube bundle. In the center of the bundle between the cold and the hot leg are suction tubes through which non-condensable gases are drawn off in the zones of lowest pressure. The supporting plates are each made of a single piece and are thus continuous, and the partition consists of individual sheet-metal parts which are connected to the supporting plates. In one embodiment, the sheet-metal parts of the partition and the supporting plate are connected to one another by indentations on each side of the sheet-metal part which faces the supporting plate and by a corresponding opening in the supporting plate. LP Feed water Heater’s pressure ratings range between 400 and 1,500 psig.
LP Feed water Heaters are designed as single zone with a condensing section or two zones with a condensing section and integral sub cooler section.
Drain coolers are employed because of heat consumption improvement in case of drain introduction into the lower heater through the level control valve. Condensing heaters without a sub cooler section have better heat consumption if the drain flows forward by using a drain pump. A drain pump is used usually for the drain of LP heaters.
High-Pressure Feed water Heater
Tube Sheet High-Pressure Heaters are designed as two zones or three zones with a condensing section, desuperheater and integral sub cooler. The use of a desuperheater reduces the terminal temperature difference (TTD) of the entire Feed water Heater. A negative TTD of up to 3°C can be achieved by the use of a desuperheater, depending on the steam inlet temperature. The tube wall temperature must be over the local saturation temperature in all operation conditions. The use of a separate cross-connected desuperheater improves the heat consumption and increases the Feed water temperature at the boiler inlet. HP Feed water heater’s pressure ratings range from 1,500 to 4,800 psig.
Drain Coolers are employed because of heat consumption improvement in case of drain introduction into the lower heater through the control valve. These types of HP Feed water Heaters have been developed to meet the increasingly severe operating conditions in large turbo generator plants. These may include high heat rates, sudden load variations and frequent start-ups and shut–downs in case of peak-load power plants.



